 Skills
Skills
Below skills are required to complete the deployment steps:
Linux Directory Structure, File Management
Pre-Requisites
Login to AWS cloud and create Linux based EC2 instance to complete the below assignment.
Deployment
- Login to the server as super user (root) and perform below
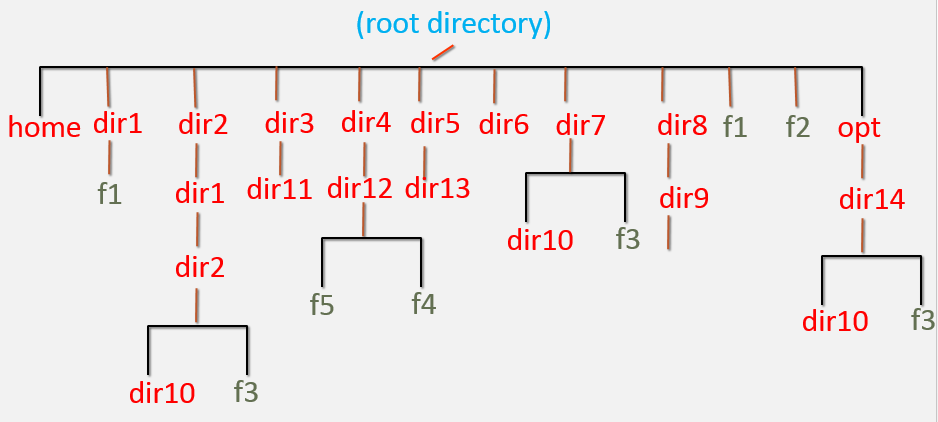
- Create the file and directory structure shown in the above diagram.
- Perform below steps
- Create directory – /dir6/dir4
- Create file – /f3
- Write this text “Linux assessment for an DevOps Engineer!! Learn with Fun!!” to the /f3 file and save it.
- Replace the “DevOps” text to “devops” in the /f3 file without using VI editor.
- Search for the pattern “Engineer” and replace with “engineer” in the file /f3 using single command using VI Editor.
- Move the file from “/dir1/f1” to “/dir2/dir1/dir2”
- Rename the file ‘/f2′ to /f4’
- Create directory – “/home/user2/dir1”
- keeping “/dir2/dir1/dir2/dir10” as present working directory; create file “/opt/dir14/dir10/f1” using relative path method.
- Move the file from “/opt/dir14/dir10/f1” to user2/dir1 directory
- Delete the directory recursively “/dir4”
- Delete all child files and directories under “/opt/dir14” using single command.
- Create file “/dir1/f2”
- Delete /dir6
- Delete /dir8
- Delete /f3
- Search for the file name ‘f4’ in the server and list all absolute paths where f4 file is found.
- Show the count of the number of files in the directory ‘/’
- Delete /dir1
- Delete /dir2
- Delete /dir3
- Delete /dir5
- Delete /dir7
- Delete /f1 & /f4
- Delete /opt/dir14
All done? still not confident? repeat the steps! Ping in the comment box below if you have completed or any challenges.
Solution
Follow the LINK to get the solution of this project.
Happy Learning!
© Edwiki Trainings – Click HERE If you are interested to learn more on Cloud & DevOps stack.








13 comments
very helpful to understand basic commands and completed tsk
completed sir
completed
completed sir
Will all steps executed successfully..?
or
we may get error for some steps.
completed Sir………..
LOGIN TO THE SERVER AS SUPER USER (ROOT) AND PERFORM BELOW
ANS :-> sudo su –
CREATE THE FILE AND DIRECTORY STRUCTURE SHOWN IN THE ABOVE DIAGRAM.
cd /
mkdir -p dir1 dir2/dir1/dir2 dir3/dir1 dir4/dir12 dir5/dir13 dir6 dir7/dir10 dir8/dir9 opt/dir14/dir10
PERFORM BELOW STEPS
CREATE DIRECTORY – /DIR6/DIR4
mkdir -p /dir6/dir4
CREATE FILE – /F3
touch /f3
MOVE THE FILE FROM “/DIR1/F1” TO “/DIR2/DIR1/DIR2”
touch /dir1/f1 ; mv /dir1/f1 /dir2/dir1/dir2
RENAME THE FILE ‘/F2′ TO /F4’
touch /f2 ;mv /f2 /f4
CREATE DIRECTORY – “/HOME/USER2/DIR1”
mkdir -p /home/user2/dir1
KEEPING “/DIR2/DIR1/DIR2/DIR10” AS PRESENT WORKING DIRECTORY; CREATE FILE “/OPT/DIR14/DIR10/F1” USING RELATIVE PATH METHOD.
cd /dir2/dir1/dir10;mkdir -p /opt/dir14/dir10; touch /opt/dir14/dir10/f1
MOVE THE FILE FROM “/OPT/DIR14/DIR10/F1” TO USER2/DIR1 DIRECTORY
cd /home ; mv /opt/dir14/dir10/f1 user2/dir1
DELETE THE DIRECTORY RECURSIVELY “/DIR4”
rm -r /dir4 (if it is empty directory we can use rmdir /dir4)
DELETE ALL CHILD FILES AND DIRECTORIES UNDER “/OPT/DIR14” USING SINGLE COMMAND.
rm -r /opt/dir14
CREATE FILE “/DIR1/F2”
touch /dir1/f2
DELETE /DIR6
rm -r /dir6
DELETE /DIR8
rm -r /dir8
DELETE /F3
rm /f3
SEARCH FOR THE FILE NAME ‘F4’ IN THE SERVER AND LIST ALL OBSOLETE PATHS WHERE F4 FILE IS FOUND.
ls -lR / | grep ‘f4’
make sure we are doing it from root directory .
SHOW THE COUNT OF THE NUMBER OF FILES IN THE DIRECTORY ‘/’
ls -1 | wc -l
DELETE /DIR1
DELETE /DIR2
DELETE /DIR3
DELETE /DIR5
DELETE /DIR7
rm -r /dir1 /dir2 /dir3 /dir5 /dir7
DELETE /F1 & /F4
rm /f1 /f4
DELETE /OPT/DIR14
rm -r /opt/dir14
completed sir.
completed.
I have completed the task, I have a doubt regarding searching for a file I used the command find /f4 to find f4 under the / directory
in the result i could see all the files and its absolute path is there a command which just gives us the result which contains only the details of file f4
[root@ip-172-31-80-55 dir10]# find / -name f4
1. Create the file and directory structure shown in the above diagram.
[root@ip-172-31-80-55 ~]# mkdir /dir1
[root@ip-172-31-80-55 ~]# touch /dir1/f1
[root@ip-172-31-80-55 ~]# mkdir -p /dir2/dir1/dir2/dir10
[root@ip-172-31-80-55 ~]# touch /dir2/dir1/dir2/f3
[root@ip-172-31-80-55 ~]# mkdir -p /dir3/dir11
[root@ip-172-31-80-55 ~]# mkdir -p /dir4/dir12
[root@ip-172-31-80-55 ~]# touch /dir4/dir12/f5
[root@ip-172-31-80-55 ~]# touch /dir4/dir12/f4
[root@ip-172-31-80-55 ~]# mkdir -p /dir5/dir13
[root@ip-172-31-80-55 ~]# mkdir dir6
[root@ip-172-31-80-55 ~]# mkdir -p /dir7/dir10
[root@ip-172-31-80-55 ~]# touch /dir7/f3
[root@ip-172-31-80-55 ~]# mkdir -p /dir8/dir9/
[root@ip-172-31-80-55 ~]# touch /f2
[root@ip-172-31-80-55 ~]# touch /f1
[root@ip-172-31-80-55 ~]# mkdir -p /opt/dir14/dir10
[root@ip-172-31-80-55 ~]# touch /opt/dir14/f3
Perform below steps
2. Create directory – /dir6/dir4
[root@ip-172-31-80-55 ~]# mkdir -p /dir6/dir4
3 Create file – /f3
[root@ip-172-31-80-55 ~]# touch /f3
4 Move the file from “/dir1/f1” to “/dir2/dir1/dir2”
[root@ip-172-31-80-55 dir1]# mv * /dir2/dir1/dir2
5 Rename the file ‘/f2′ to /f4’
[root@ip-172-31-80-55 dir1]# mv /f2 /f4
6 Create directory – “/home/user2/dir1”
[root@ip-172-31-80-55 dir1]# mkdir -p /home/user2/dir1
7 keeping “/dir2/dir1/dir2/dir10” as present working directory; create file “/opt/dir14/dir10/f1” using relative path method.
[root@ip-172-31-80-55 dir10]# touch ../../../../opt/dir14/dir10/f1
8 Move the file from “/opt/dir14/dir10/f1” to user2/dir1 directory
[root@ip-172-31-80-55 dir10]# mv f1 /home/user2/dir1
9 Delete the directory recursively “/dir4”
[root@ip-172-31-80-55 dir10]# rm -r /dir4
rm: descend into directory ‘/dir4’? y
rm: descend into directory ‘/dir4/dir12’? y
rm: remove regular empty file ‘/dir4/dir12/f5’? y
rm: remove regular empty file ‘/dir4/dir12/f4’? y
rm: remove directory ‘/dir4/dir12’? y
rm: remove directory ‘/dir4’? y
10 Delete all child files and directories under “/opt/dir14” using single command.
[root@ip-172-31-80-55 dir10]# rm -rf /opt/dir14/dir10
11 Create file “/dir1/f2”
[root@ip-172-31-80-55 dir10]# touch /dir1/f2
12 Delete /dir6
[root@ip-172-31-80-55 dir10]# rm -r /dir6
13 Delete /dir8
[root@ip-172-31-80-55 dir10]# rm -r /dir8
14 Delete /f3
[root@ip-172-31-80-55 dir10]# rm -r /f3
15 Search for the file name ‘f4’ in the server and list all obsolete paths where f4 file is found.
[root@ip-172-31-80-55 dir10]# find / -name f4
[root@ip-172-31-80-55 dir10]# find / -name f3
/dir2/dir1/dir2/f3
/dir7/f3
16 Show the count of the number of files in the directory ‘/’
[root@ip-172-31-80-55 /]# ls | wc -l
28
17 Delete /dir1
[root@ip-172-31-80-55 /]# rm -rf /dir1
18 Delete /dir2
[root@ip-172-31-80-55 /]# rm -rf /dir2
19 Delete /dir3
[root@ip-172-31-80-55 /]# rm -rf /dir3
20 Delete /dir5
[root@ip-172-31-80-55 /]# rm -rf /dir5
21 Delete /dir7
[root@ip-172-31-80-55 /]# rm -rf /dir7
22 Delete /f1 & /f4
[root@ip-172-31-80-55 /]# rm -rf /f4
[root@ip-172-31-80-55 /]# rm -rf /f1
23 Delete /opt/dir14
[root@ip-172-31-80-55 /]# rm -rf /opt/dir14
Hi Sir,
Please check and let me knoe is correct or not
Yes completed